Implementation of Interface of Stepper Motor with Microcontroller ,Hardware and Software sides
Now we will proceed towards the real implementation of interface of stepper motor with microcontroller and will complete its hardware and software sides one by one.
Hardware of Stepper Motor (Electronics Circuit design)
The hardware of this project is consists of three major portion as described below:
- Microcontroller: The necessary components used to operate the microcontroller to do some useful tasks in accordance with the coding in it.
- The serial communication circuit around RS-232
- Power connection and Power driver circuit of stepper motor which accept commands from microcontroller and operate the stepper motor accordingly.
Power Driving Circuit for stepper Motor
It is normal practice that the steppers motors draw high currents as compared to other motor of same size. It is therefor need to be
operated through a power driver circuit. In our case the stepper motor we are using in this project takes 0.4 to 2.0
Ampere current i.e. 0.2 ampere per coil in pull-out state and 1 ampere per coil
in hold state. Therefor we have designed a power driver circuit for it which includes TIP 121 NPN to provide the high current to the
coils of stepper motor. The TIP-121 NPN transistors is actually a Darlington Silicon power transistor. The electronics connection diagram has
been shown in figure below.
 |
| Power driver circuit diagram for Stepper motor connection with microcontroller At89c51 |
Complete circuit diagram of the Microcontroller Project:
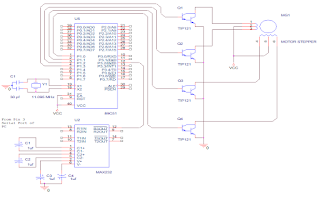 |
| stepper motor controller circuit diagram 8051 RS232 serial port |
Software of Stepper motor project:
- The program written C++ language to be run inside PC for serial communication with Microcontroller for the effective control of stepper motor.
- The program written in assembly language for microcontroller to implement the desire task.
The C++ Code for serial communication and Stepper motor control
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 | #include<constream.h> // Builin Libraries of the compiler #include<stdio.h> #include<dos.h> #define COM1 0x2F8 // serial port number void send_data(char rotations, char steps, char control,char delay_low,char delay_high); void main(){ int rotations,steps,control,sps,*ptr; int i,j,k,l,m; float rpm; char rots,stps,ctrl,*chr_ptr,delay_low,delay_hi; /* port Initialization*\ outportb(COM1+1, 0); // Turn off interrupts - port1 outportb(COM1+3, 0x80); // Set DLAB ON outportb(COM1+0, 0x0C); // Set baud rate - Diviser latch low byte outportb(COM1+1, 0x00); // Set baud rate - Diviser latch high byte outportb(COM1+3, 0x03); // 8-bit no parity mode outportb(COM1+2, 0xC7); // FIFO Control Register outportb(COM1+4, 0x0B); // Turn on DTR, RTS and OUT2 clrscr(); printf("\n Control Program"); printf("\n ====== =======\n\n\n\n"); do{ printf("Enter No of rotation [0-255] "); scanf("%d",&rotations); } while(rotations<0 || rotations>255); rots=(char)rotations; do{ printf("\nEnter No of Steps [0-200] "); scanf("%d",&steps); } while(steps <0 || steps>200); stps=(char)steps; do{ printf("\nEnter RPM [60-240] "); scanf("%f",&rpm); } while(rpm<60.00 || rpm>240.00); do{ printf("\nEnter Direction"); printf("\n0 for Clockwise"); printf("\n1 for Counter Clockwise "); scanf("%d",&control); } while(control <0 || control >1); ctrl=(char)control; sps=int(1000000/(rpm*6/1.8)); sps=-0.9*sps; ptr=&sps; chr_ptr=(char *)ptr; delay_low=*chr_ptr; delay_hi=*((char *)chr_ptr+1); // call_send data to send data to serial port send_data(rots,stps,ctrl,delay_low,delay_hi); getch(); } void send_data(char rots,char stps, char control,char delay_low,char delay_high) { outportb(COM1,delay_high); //send delay high byte for (int i=1 ;i<1000;i++); outportb(COM1,delay_low); //send delay low byte for (i=1 ;i<1000;i++); outportb(COM1,control); //send control byte for (i=1 ;i<1000;i++); outportb(COM1,stps); //send number of steps for (i=1 ;i<1000;i++); outportb(COM1,rots); //sendt number of rots } |
The Assembly Language program for Microcontroller 8051.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 | ;MAIN PROJECT PROGRAM ORG 00H SJMP MAIN; DIRECTING PROGRAM FLOW TO MAIN ORG 0023H LJMP SP_ISR; DIRECTING SERIAL PORT INTERUPPT TO ROUTINE ORG 0030H MAIN: MOV IE,#90H; ENABLE SERIAL PORT INTERRUPT MOV SCON, #50H; SET SERIAL PORT MODE 1 AND ENABLE RECIVE DATA MOV TMOD, #21H; SET TIMER 1 IN MODE 2 AND TIMER 0 IN MODE 1 MOV TH1, #-3; SET TIMER 1 HIGH BYTE FOR 9600 BAUD RATE MOV R0,#05H; SET REGISTER R0-R5 TO THEIR INITIAL VALUES MOV R1,#00H; MOV R2,#00H; MOV R3,#00H; MOV R4,#00H; MOV R5,#00H; CLR F0; CLEAR THE BIT F0; MOV A,#96H; LOAD ACCUMULATER WITH INITIAL CONDITION SETB TR1; START TIMER 1 RUN: JNB F0,RUN; WAIT UNTIL F0 GET SET JMP ROTS; JUMP TO ROTS ROUTINE WHEN F0=1 STP: MOV B,R2; MOVE THE CONTENTS OF R2 TO R6 MOV R6,B; MOV R2,#00H; JUMP TO STEP: TO COMPLETE THE NO OF STEPS JMP STEPS; FINISH: CLR F0; CLEAR F0 WHEN ALL THE ROTATIONS AND STEPS ARE COMPLETE SETB P2.0; SJMP RUN; GO TO RUN AND WAIT TILL THE NEW INPUT FROM PC IS RECIVED ROTS: INC R1; DJNZ R1,GO_ROTS; CHECK IF NO OF ROTATIONS ARE ZERO IF YES GO FOR STEPS JMP STP; GO_ROTS: INC R3 DJNZ R3, CLK_WSE_ROT; GO FOR CLOCK WISE ROTATIONS JMP ANT_CLK_ROT; GO FOR ANTI-CLOCK WISE ROTATIONS STEPS: INC R6 DJNZ R6,GO_STEPS; CHECK IF NO: OF STEPS ARE ZERO IF YES GO FOR FINISH JMP FINISH; GO_STEPS: INC R3 DJNZ R3, CLK_WSE; GO FOR CLOCK WISE STEPS JMP ANT_CLK; GO FOR ANTI-CLOCK WISE STEPS CLK_WSE_ROT: MOV R6,#200; LOAD R6 WITH INITIAL VALUE OF 200 STEPS FOR ONE STEPS SP1: MOV P1,A; LOAD PORT WITH INITIAL VALUE RL A; GENERATE NEW VALUE FOR PORT 1 FOR CLOCKWISE DIRECTION RL A; CALL DELAY; WAIT FOR DELAY BETWEEN TWO STEPS DJNZ R6,SP1; CHECK IF ONE ROTATION IS COMPLETE DJNZ R1,CLK_WSE_ROT; CHECK IF TOTAL ROTATIONS ARE COMPLETE JMP STP ANT_CLK_ROT: MOV R6,#200; LOAD R6 WITH INITIAL VALUE OF 200 STEPS FOR ONE STEPS SP2: MOV P1,A; LOAD PORT WITH INITIAL VALUE RR A; GENERATE NEW VALUE FOR PORT 1 FOR ANTI_CLOCKWISE DIRECTION RR A; CALL DELAY; WAIT FOR DELAY BETWEEN TWO STEPS DJNZ R6,SP2; CHECK IF ONE ROTATION IS COMPLETE DJNZ R1,ANT_CLK_ROT; CHECK IF TOTAL ROTATIONS ARE COMPLETE JMP STP; CLK_WSE: JMP CLK_WSE_STEPS; CLK_WSE_STEPS: MOV P1,A; RL A; RL A CALL DELAY; DJNZ R6,CLK_WSE_STEPS; JMP FINISH ANT_CLK: JMP ANT_CLK_STEPS; ANT_CLK_STEPS: MOV P1,A; RR A; RR A; CALL DELAY; DJNZ R6,ANT_CLK_STEPS; JMP FINISH; DELAY: MOV TH0,R5; LOAD TIMER 1 WITH DELAY VALUES MOV TL0,R4; SETB TR0; HERE: JNB TF0,HERE; WAIT FOR TIMER OVERFLOW CLR TR0; CLR TR0 CLR TF0; STOP TIMER1 RET; RETURN TO THE CALLING INSTRUCTION SP_ISR: MOV @R0,SBUF; RECIVE DATA FROM SERIAL PORT CLR RI; CLEAR RECIVE INTERRUPT BIT DJNZ R0,RETU; CHECK IF ALL THE FIVE DATAS ARE RECIVED MOV R0,#05; LOAD R0 WITH INTIAL VALUE CLR P2.0 SETB F0; SET F0 RETU: RETI; RETURN FROM INTERRUPT END |
No comments:
Post a Comment
Please ask if you have any question regarding the programming of MCU, or have any problem in development of your electronics project. microcontroller51.blogspot.com