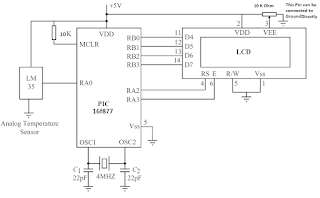
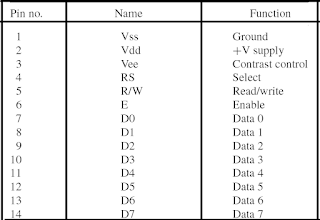
Introduction of Printer Port and MCU controller for Solenoid Valve
In this project our task was to develop a complete circuit to control solenoid using PC interface. Computer system is interfaced with microcontroller with the help of parallel port. This project is to develop a complete system to control Solenoid Valve System. The main part of this project is the interfacing of microcontroller to the PC and with the other devices. The data is provided by the pc to the microcontroller and this data is the provided to the DAC which generates different voltages levels according to the input given this data is the provided to the OPAM which provides us the required voltage levels. This project is divided in to four parts or stages. Which are as under:
- PC and Parallel Port Interfacing
- Designing Circuit and selection of components or Devices
- Microcontroller Programming or Coding
- Solenoid valves controlling testing
Overview of the Project
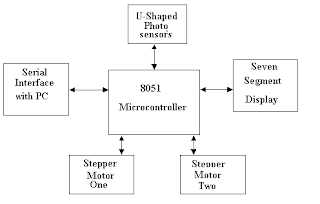
Before giving the detail description of each equipment used, it is important to describe the general overview over the project circuitry, that is how the data starts from PC and being received by solenoid in the end. First of all the data from PC is send to LATCH 373 using parallel port of PC. The data is received on LATCH on pins D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8 from parallel port pins 2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 respectively. Pin 10 is grounded and pin 20 is been given VCC 20 volts. The is transferred to micro controller on port-I on pins 1-8. The corresponding pins of latch are Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4, Q5, Q6, Q7, and Q8 respectively. The data is then transmitted To port 2 on pins 21 to 28. The next step is to send data on DAC-0800. The data from micro controller pin 2 is then received by DAC on pins 12 to 5 respectively. Then data is received by op-amp on pins 2 and 3 from DAC pins 3 and 4 respectively. Finally, the data received by op-amp is connected to solenoid, which has different variations as requirements of user. This was a brief summary of the data from PC till the last object solenoid. The diagram of above procedure is given below.
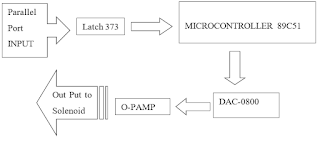 |
| Block Diagram of Printer Port Interface to MCU to Control Solenoid |
PC Parallel Port Interfacing
Parallel port of computer is the one of oldest port available with PC to interface devices with computer through it. The interface through printer port is easy for developing computer-controlled system and projects. This feature of parallel port makes programming of parallel port convenient in electronics hobbyist world. The parallel or printer port is very often used in robots, test equipment, microcontroller programmers, home automation, etc. The primary use of parallel port was to connect printers with computer as it was designed for this purpose, thus, it is usually also called Printer Port. The parallel port connector can be searched at the rear side panel of PC. It is a 25-pin female DB25 connector to which normally printer was connected. The PCs have only one parallel port normally. Additional Parallel Ports can be added inserting ISA/PCI cards.
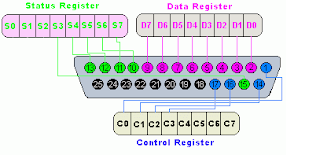 |
| DB25 PIN Connection of Printer Port |
We will use parallel port here to connect it to the microcontroller through the latches. The data from PC will be latched and then forwarded to the microcontroller. A simplified diagram of a parallel port along with its pin configuration is given blow. The pin outs of connector is shown in the picture below. Parallel Port Pins The data input and output lines in DB25 connector of parallel port can be divided in to three sub-groups, which are listed as below:
- Data lines (data bus)
- Control lines
- Status lines
The brief introduction of these groups is as, the data is transferred over data I/O lines, Control lines are used to control the peripheral. The peripheral can return some status signals back to computer, for this purpose the Status lines are used. These I/O lines are connected to Data, Control and Status registers internally inside PC.
Latch 373 Description
Latch LMS-373 is 20 pin IC. Which is used here to transfer the data from PC to controller. It received the data on clock pulses. When the enable (pin 11) is taken low the output will be latched at the level of the data that was set up. The eight flip-flops of the 74LS373 are edge-triggered D-type flip flops. When there is the positive transition of the clock, the Q outputs of flipflop/ latch will be set to the logic level which was at D inputs at that time.. The output control of latch does not affect the internal operation of the latches . That is, the old data on the latch can be retained or new data can be entered to it even when the outputs are switched off.
ATMEL89C51 Description
The AT89C51 is a low power, high performance 8-bit micro controller with 4K bytes of programmable and erasable read only memory (PEPROM). The device is manufactured using ATMEL’s high density nonvolatile memory technology and comparable with the industry of MCS-51TM instruction set and pinout. The on chip flash can be reprogrammed by first erasing the last program using ultra violet rays and then write new program on it using software.
OJ0800 DAC
A digital to analog converter (DAC) is an integrated circuit that converts a digital signal input to an analog output voltage or current that is the binary weighted equivalent of the digital input code. Modern DAC s are, effectively, an array of matched current sources optimized for frequency domain performance .To handle both strong and week signals DACS require large dynamic range. Beside these there are a number of the DC parameters such as integral nonlinearities (INL) and differential nonlinearities (DNL), that are considered important because of their influence on SFDR parameters .The resolution of the DAC is dependent upon the type of the DAC, whether it is 16 bit or 8 bit, higher the number of bits smaller will be the quantization error. In our project we have used CJ0800, which is an 8 bits DAC .So the number of quantization levels are equal to 256 levels. The ratio of the input voltage range to the number of quantization levels will determine the output voltage, but remember that larger the input voltage range greater will be the quantization error. Several factors influence the selection of the DACs
- DAC resolution
- DAC dynamic specifications
- Operating frequencies
- Type of the signal
- Supply voltages
- Cost
DACs error will add to the error caused by the resolution of the converter. A given DAC may or may not include the dc or ac error specifications. Offset error is critical in dc applications. For this reason, a buffer OP AMP must be selected that does not contribute to the problem its own offset voltages should be much less than that of the converter. The settling time of the DAC is time between the switching of the digital inputs of the converter and the time when Its output reaches its final value and remains within a specified error band or the tolerance band. It is the reciprocal of the maximum D/A conversion rate.
LM741 Operational Amplifier General Description
An operational amplifier is an integrated circuit that produces an output voltage that is An amplified replica of the difference between the two input voltages. An op amp can be characterized by following transfer function. where is the open loop gain of the operational amplifier . Most op amps are of monolithic type and there are dozens of different manufacturers. Op Amps are used in conjunction with other circuit components such as resisters and capacitors to perform various mathematical operations as well as a multitude of tasks. Two types of inputs are available on the integrated IC such as LM741 which we used in our project. These are named as inverting and non-inverting inputs. The op amp is ideally completely insensitive to the voltage components, which are common to the inputs. The open loop gain is a positive dimensionless constant and is usually very large, often in the range of hundreds of thousands at very low frequencies (0-30) Hz. Op Amps enter the saturation region when operated in the open loop so that a closed loop operation is always recommended, as open loop operations causes severe distortion of the signal. In the feed back configurations the gain of the amplifier is only dependent on the external components (capacitors and resistors) in our project we used the op amp as a non-inverting amplifier in order to get the positive output voltage required for the solenoid operation. The gain of a non-inverting amplifier is calculated using gain equation. Under these conditions op amp is operating as a closed loop system and the fraction of the output voltage is feed back to the inverting input terminal and is called the feed back factor.
CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IDEAL OP AMP
The ideal characteristics of ideal op amp are given as follow; • Infinite impedance • Zero output impedance • Infinite open loop gain The op amp diverges from the ideal characteristics due to many reasons. There are even more severe problems with op amps namely CMRR and input and offset voltages nulls.
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGES
All op amps require a small voltage between their inverting and no inverting inputs to balance the mismatches due to unavoidable process variations. The require voltage is known as input offset voltage and is normally modeled as no inverting input deriving source. The input offset voltage is of concern anytime when dc accuracy is required for the circuit. The method to null the offset voltages is to use external components to null the inputs on a single op amp chip. A potentiometer is connected between the null inputs with adjustable terminal connected to the negative supply through the series of the resisters, the input offset voltages can be nullified by shorting the inputs and adjusting the potentiometer until output voltage is zero.
Solenoid Valve
Solenoid is defined as a device used to control the motion of an iron bar according to the voltage applied to it. A coil of insulated wire is the main component of solenoid in which a magnetic field is produced with the flow of electric current through the coil. A coil which is surrounding a movable iron core which is pulled when the coil is electrically energized. This movement can be used to perform some specific mechanical work, such as opening a mechanical process valve, or operate an electrical switch. Cylindrical coil having larger length as compared to diameter of coil. When the current is passed through the coil of the solenoid, it comes a magnet until the current is there. The magnetic field is established due to passing current from the coil of solenoid. Therefore, it can be said that the solenoids are electromagnetic switches. When electricity passes through the solenoid, the magnetic field formed which forces to move a metal piston. The piston of solenoid is usually connected or attached to a mechanical mechanism that performs the desired specific function. The movement of metal piston causes actually to execute the application work. The application work is like operation of a mechanical valve, operation of a switch, or mechanical linkage process. In engineering fields, the solenoid is a electro-mechanical device that converts electrical energy into some where linear motion of a part. The Solenoids are usually developed or constructed to use electricity for control of compressed air, or pressurized fluids i.e. the hydraulic solenoids. The Solenoid valves are operated with electric power supply and used in variety of industrial application where the fluids are required to control automatically. Parallel to the technologic development its fields of usage have been increasing. The Solenoid valves have been derived from the principal that a magnetic field, forced by the electric energy with the help of a coil, moves some mechanical parts. Depending upon the use of project or system or application, the Solenoid valves can be developed with 02 or more ways and in different sizes as per needs. The electric supply to solenoid can be 6, 12, 24, 48, 72, 110, 220 VAC or VDC according to application or system or project usage. In Solenoid Valves the widely used body material is brass, but stainless steel, bronze, cast iron, steel or plastic body valves can be produced as well. According to the working principle of the Solenoid Valves, these can be classified into two main classes as Direct Acting Solenoid and pilot operated Solenoid. The Solenoid valves can also be classified in accordance to the fluid types control by these. The Solenoid Valves are also designed as ON or OFF type valves subject to availability of electricity. Thus, the solenoid valves can be the valve which are Normally Open or Normally Closed. Whenever we are concerned with the design of the solenoid then the major concerns are of these two areas. Determining the number of turns and the design related to electrical parameters and Design related to the mechanical parameters.
Software for Parallel Port Interface
/* Include the right header file, the library files*/ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> /* main program starts here*/ void main(void) { clrscr(); // Clear the screen of computer int data=0x378; \\ initializing the parallel port int n; \\ Declaring variables char ch; // declaration of a temporary variable do{ \\ multiple input loop cout<<"\t\tInput any hex value to be transfered\n"; cin>>hex>>n; cout<<"The Data is "; cout<<hex<<n<<endl; outportb(data,n); \\ sending data on port cout<<"\t\t\tPress any key to continue\n"; cout<<"\t\t\tPress e twice to exit\n"; ch=getche(); // get a character from keyboard clrscr(); } while(ch!='e'); \\ program exit condition check getch(); }